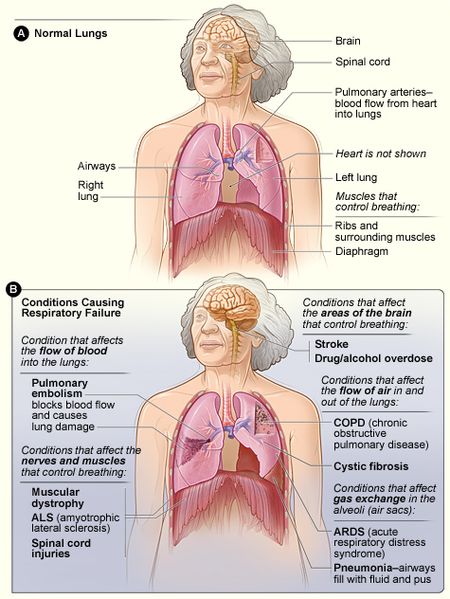
oxygen flow rate for pneumonia
NHF is most commonly used oxygenating patients with severe acute respiratory failure from medical conditions such as pneumonia or bronchiolitis in children. The value of clinical features in differentiating between viral pneumococcal and atypical bacterial pneumonia in children.

Pneumonia Bipap Secretions And Hfnc New Lessons From Florali
Low flow masksA concentration of up to 60 can be achieved with moderate oxygen flow rates 6-10 lmin and these masks are used mainly in type I respiratory failure for example pulmonary oedema pulmonary embolus.
. 60 PaO 2 32mmHg in unrepaired congenital cyanotic heart disease. This gives the user peace of mind knowing that their supplemental oxygen therapy for pneumonia is always spot on. The oxygen flow rate and.
Venturi masks are available in different forms which can convey and deliver low and fixed concentrations of oxygen at 25 30 35 and 40 percent. This includes a high-flow nasal cannula a high-flow source with systems regulating the flow and the FiO 2 a humidifier system and heated tubing. Supplemental oxygen delivers to the lungs air that is 99 pure oxygen versus the air we normally breathe made up of about 20 oxygen.
70 PaO 2 37 mmHg in patients who have had cardiac surgery of their congenital cyanotic heart disease. A study revealed that for every 10 Lmin increase in the gas flow rate PEEP increased by 0510 cm H 2 O and the flow rate of 60 Lmin could produce 87 cm H 2 O of PEEP in the pharyngeal. Green or yellow phlegm indicating the need for antibiotics.
For example patients commonly use a flow rate of 2 liters per minute but the flow rate varies by each patients needs. Oxygen is allowed to flow from the cylinders in the form of a jet through a narrow system and the base of the mask is what creates negative pressure. Now you know how to check your oxygen saturation using a pulse oximeter and also how to set your oxygen concentrator flow to the right dosage of oxygen whether its being used by 1 or 2 people.
However the effectiveness of oxygen therapy as a treatment for pneumonia is not well known. The model is based on five key factors affecting oxygen demand. Treatment for pneumonia includes antibiotics rest fluids.
At low oxygen flow rates. The normal flow rate of oxygen is usually six to 10 litres per minute and provides a concentration of oxygen between 40-60. Goal of Oxygenation.
Any other changes to your normal breathing patterns. Oxygen therapy is widely used in the treatment of lung diseases. Pneumonia With Oxygen Levels Above 95 As Measured By A Pulse Ox BREAKING.
For example if your doctor determines that your safe oxygen saturation level should be 92 or above they may advise you to increase your oxygen flow rate if your saturation drops below 92. We sought evidence to support or refute the practice. The rate of intubation among 99 patients given high-flow oxygen was 343 compared with 510 among the 100 patients assigned to conventional oxygen therapy hazard ratio HR 062.
Thirteen patients on high-flow oxygen had suspected bacterial pneumonia as did. However a target SpO 2 of 92 to 96 seems logical considering that indirect evidence from patients without COVID-19 suggests that an SpO 2 of 96 may be harmful. There are two important things to consider when delivering supplemental oxygen to your patient.
At present oxygen therapy for individuals with pneumonia is commonly prescribed. Among outpatients with pneumonia oxygen saturations. This is why they are often referred to as MC medium concentration masks as 40-60 is considered to be a medium concentration of oxygen.
Giving a flow rate higher than 6lmin will damage your patients nasal passage. These parameters were varied over a wide range of values to generate simulation results for different settings. A bluish tinge to your fingernails or lips a sign.
Up to 100 humidified oxygen can be delivered at a high flow rate up to 60 Lmin that meets inspiration flow rates minimizing room air entrainment. The flow rate is how many liters of oxygen per minute your device delivers. DENNIS ITUMBI RUSHED TO ICU AFTER DEVELOPING PNEUMONIA LEADING TO LOW OXYGEN LEVELS These patients can be safely treated at home with antibiotics as long as they watch their symptoms.
The median time to recovery in the two groups was 11 vs 14 days HR 139. Annual pneumonia admission rate hypoxaemia prevalence degree of seasonality treatment duration and oxygen flow rate. Ideally youll want to see numbers between 95 and 100.
A flow rate of 2 liters per minute increases the FiO2 from 21 percent room air to 28. Korppi M Don M Valent F Canciani M. How much FiO2 you receive from your oxygen concentrator depends on your flow rate.
If your levels are below 90 you have a very low oxygen saturation and its going to help a lot when you use the concentrator. Adult HFNO can either be delivered by the mechanical ventilator or by stand-alone systems such as Optiflow R which require a permanent power source because they are. 5 This system provides high-flow 30 to 60 LPM oxygen that is heated to body temperature 37 o C and is fully saturated 100 relative humidity with minimal or no rainout in the tubing.
Experience in the use of HFNO in coronavirus pneumonia is limited and an important disadvantage for the resource-poor setting is the very high oxygen flow of up to 60 Lminute needed. It eliminates wastage and maximizes oxygen for pneumonia patients. The optimal oxygen saturation SpO 2 in adults with COVID-19 who are receiving supplemental oxygen is unknown.
Our results indicate a hospital admission threshold of. In many cases pneumonia patients whose symptoms are not life-threatening would be candidates to receive oxygen via an oxygen concentrator which is less expensive than a tank or cylinder. However do not adjust your oxygen flow rate or the amount of time you us e supplemental oxygen without.
Total oxygen volume peak patient load and hours. 94 - 98 PaO 2 between 80 and 100 mmHg in patients without cyanotic congenital heart disease or chronic lung disease. To determine the effectiveness and safety of oxygen therapy in the treatment of pneumonia in adults older than 18 years.
The optimal oxygen saturation SpO 2 in adults with COVID-19 who are receiving supplemental oxygen is unknown. This conserver produces an operating pressure range of 500-3000 psi and allows patients to ambulate longer than with a continuous flow regulator on the same cylinder. The provider sets the flow rate and Fi02.
It is unlikely that the FiO2 will increase if the flow rate is increased above 10.
Respiratory Support For Acute Intensive Care Clinician S Brief
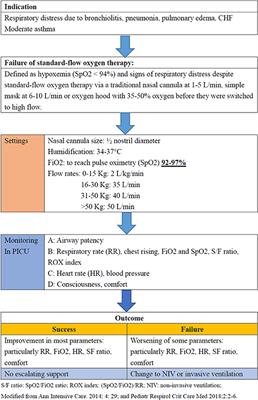
Frontiers High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy In Children With Acute Respiratory Distress With Hypoxia In A Pediatric Intensive Care Unit A Single Center Experience Pediatrics

Community Acquired Pneumonia In Adults Diagnosis And Management American Family Physician

Environmental Contamination In The Isolation Rooms Of Covid 19 Patients With Severe Pneumonia Requiring Mechanical Ventilation Or High Flow Oxygen Therapy Journal Of Hospital Infection

Assessment Of Pulmonary Arterial Circulation 3 Months After Hospitalization For Sars Cov 2 Pneumonia Dual Energy Ct Dect Angiographic Study In 55 Patients Eclinicalmedicine
Oxygen Provision To Severely Ill Covid 19 Patients At The Peak Of The 2020 Pandemic In A Swedish District Hospital

High Flow Nasal Oxygen A Safe Efficient Treatment For Covid 19 Patients Not In An Icu European Respiratory Society

Pneumonia Bipap Secretions And Hfnc New Lessons From Florali
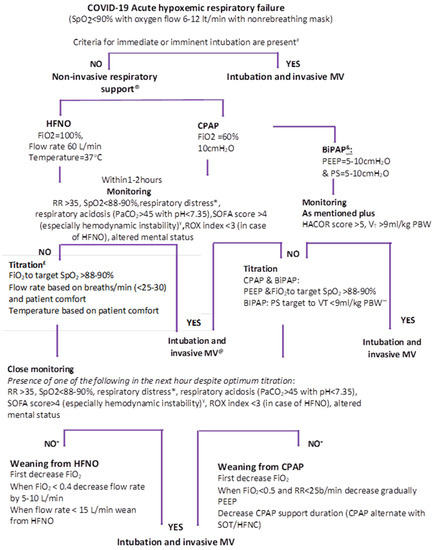
Jpm Free Full Text The Role Of Noninvasive Respiratory Management In Patients With Severe Covid 19 Pneumonia Html

High Flow Noninvasive Ventilation And Awake Nonintubation Proning In Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 With Respiratory Failure Chest

Is Oxygen An Effective Treatment Option To Alleviate The Symptoms Of Breathlessness For Patients Dying With Covid 19 And What Are The Potential Harms The Centre For Evidence Based Medicine

High Flow Oxygen Through Nasal Cannula In Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure Nejm

Non Invasive Respiratory Support In The Treatment Of Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure Secondary To Covid 19 Related Pneumonia European Journal Of Internal Medicine

High Flow Nasal Cannula Versus Conventional Oxygen Therapy In Emergency Department Patients With Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema A Randomized Controlled Trial Annals Of Emergency Medicine

Pneumonia Bipap Secretions And Hfnc New Lessons From Florali
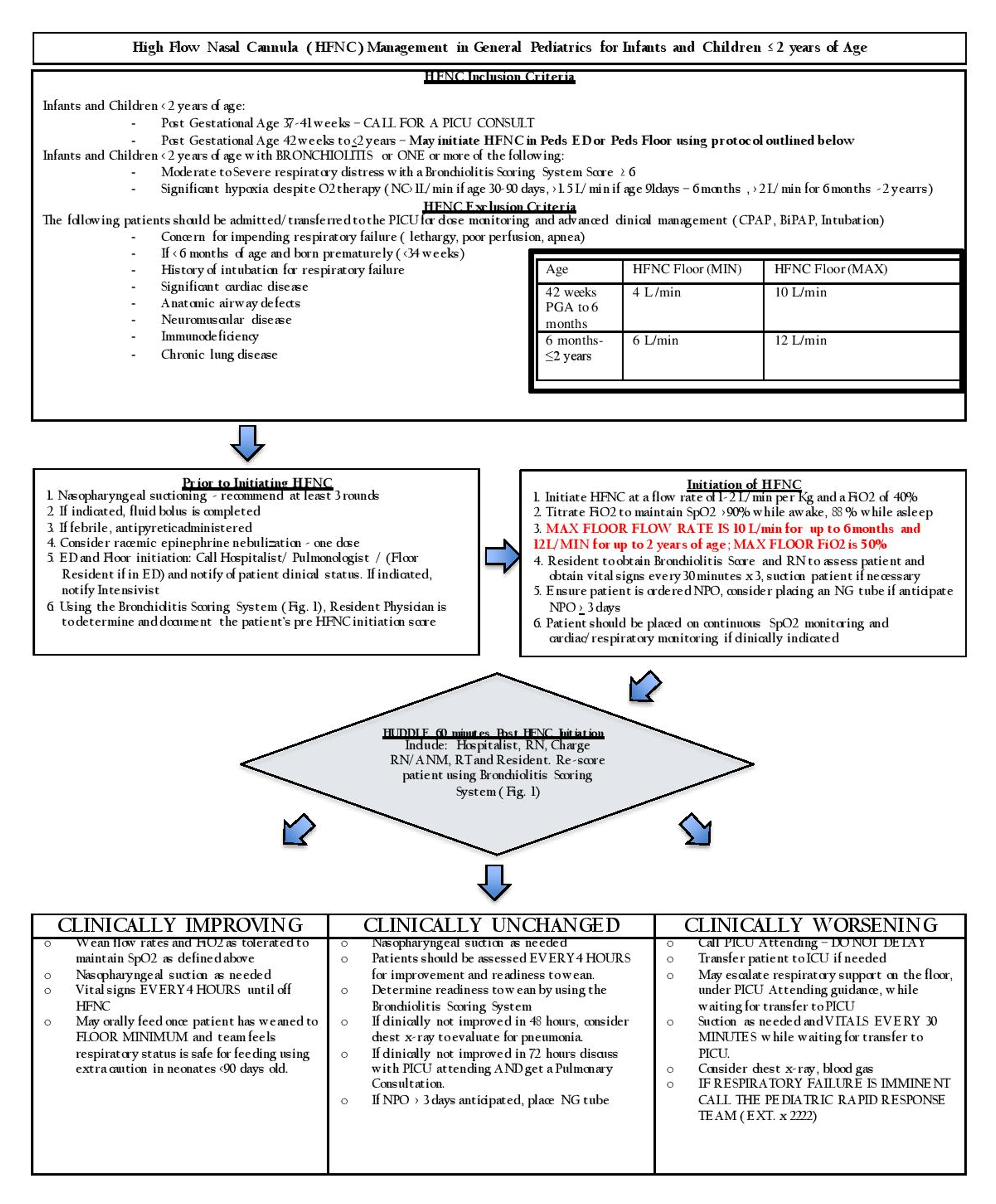
Cureus The Use Of High Flow Nasal Cannula And The Timing Of Safe Feeding In Children With Bronchiolitis

Corticosteroids In Patients Hospitalized For Covid 19 Pneumonia Who Require Oxygen Observational Comparative Study Using Routine Care Data Clinical Microbiology And Infection